DIABETES FACTS

DIABETES FACTS
The word diabetes was coined by “Aretaeus” of Cappadocia. The word is derived from the Greek ‘diabanein’, which literally means “passing through” or “siphon”, a reference to one of the main symptoms of diabetes – excessive urine discharge.
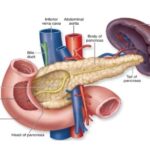
Diabetes is defined as a metabolic disorder where in human body does not produce or properly use insulin, a hormone that is required to convert sugar, starches and other food into energy.
Diabetes – “Siphon” 2nd century AD – Areteus of Cappadocia
Mellitus – “Honey” 1776, by Matthew Dobson
It is characterized as a condition whereby the body is not able to regulate levels of glucose (a sugar) in the blood, resulting in too much glucose being present in the blood.
TYPES OF DIABETES
As you are aware, there are three types of diabetes:
- Pre diabetes
- Type I diabetes
- Type 11 diabetes
- Gestational Diabetes
- Prediabetes
Prediabetes is a serious health condition where blood sugar levels are higher than normal, but not high enough yet to be diagnosed as type 2 diabetes. Prediabetes doesn’t always have symptoms, so it’s important to get blood sugar levels tested, especially if you’re at high risk. Losing weight, exercising regularly and eating healthy can reverse prediabetes and prevent Type 2 diabetes.
TYPE I DIABETES
In Type 1,
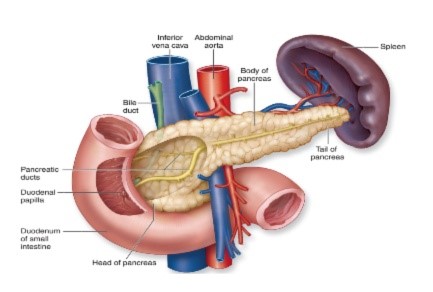
the body is unable to produce any insulin. Type 1 diabetes is an autoimmune disease. An autoimmune disease results when the body’s system for fighting infection (the immune system) turns against a part of the body. In diabetes, the immune system attacks the insulin-producing beta cells in the pancreas and destroys them. The pancreas then produces little or no insulin.
At present, scientists do not know exactly what causes the body’s immune system to attack the beta cells, but they believe that autoimmune, genetic, and environmental factors, possibly viruses, are involved. In a Type 1 diabetic, the beta cells produce little or no human insulin. When this happens the blood sugar level begins to rise to a dangerous level.
Type 1 diabetes develops most often in children and young adults, but the disorder can appear at any age. Symptoms of type 1 diabetes usually develop over a short period, although beta cell destruction can begin years earlier.
Symptoms include increased thirst and urination, constant hunger, weight loss, blurred vision, and extreme fatigue. If not diagnosed and treated with insulin, a person can lapse into a life-threatening diabetic coma, also known as diabetic ketoacidosis.
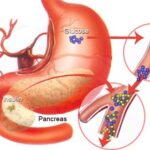
In Type 2 diabetes, not enough insulin is produced or the insulin that is made does not work properly.
TYPE II DIABETES
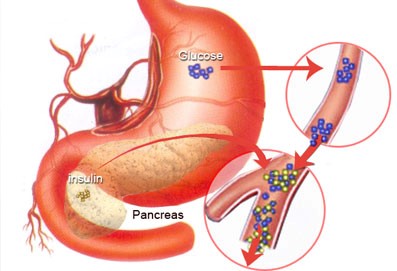
common form of diabetes is type 2 diabetes. Type 2 diabetes is often part of a metabolic syndrome that includes obesity, elevated blood pressure, and high levels of blood lipids.
When type 2 diabetes is diagnosed, the pancreas is usually producing enough insulin, but, for unknown reasons, the body cannot use the insulin effectively, a condition called insulin resistance. After several years, insulin production decreases. The result is the same as for type 1 diabetes–glucose builds up in the blood and the body cannot make efficient use of its main source of fuel.
GESTATIONAL DIABETES

- Gestational Diabetes Mellitus (GDM)
- Pregestational Diabetes Mellitus (Pre-GDM)
Gestational Diabetes Mellitus (GDM)
Diabetes detected for the first time during pregnancy – 90 %
Over the next 2-3 decades there will be 80 million reproductive-age women with Diabetes of this 20 million will be in India.
GESTATIONAL DIABETES MELLITUS (GDM)
- GDM is defined as carbohydrate intolerance with onset or recognition during pregnancy.
- Women diagnosed to have GDM are at increased risk of future diabetes predominantly type 2, as are their children.
- GDM offers an important opportunity for the development, testing and implementation of clinical strategies for diabetes prevention.Get all the advice and treatment for GDM at our clinicUncontrolled diabetes during pregnancy leads to
2 problems
- Increased maternal & foetal morbidity/mortality
- Higher rate of foetal malformationsUnder the expert care at our clinic, such issues can be avoided with proper consultation.
- Pre-eclampsia
- Pyelonephritis, other infections
- Preterm labor
- Abortions
- Traumatic delivery
- Overt diabetes
Foetal Complications
- Congenital anomalies
- IUGR
- Increased still-births
- Macrosomia
- Increased Respiratory problems
- Jaundice
- Long term effects – Diabetes
- Screen pregnant women early
- Pre pregnancy counselling
- Initiate treatment early
- Euglycaemia is the goal in pregnancy
- Frequent Monitoring
- Expert Guidance is a must
- Post partum monitoring
Get all the advice and treatment for GDM at our clinic
Risk factors – Diabetes risk factors include the following:
Overweight (body mass index ≥25 kg/m2).
Family history diabetes mellitus in a first-degree relative.
Habitual physical inactivity.
Belonging to a high-risk ethnic or racial group (eg, African-American, Hispanic, Native American, Asian-American, and Pacific Islanders).
History of delivering a baby weighing >4.1 kg (9 lb) or of gestational diabetes mellitus.
Hypertension (blood pressure ≥140/90 mmHg).
Dyslipidemia defined as a serum high-density lipoprotein cholesterol concentration ≤35 mg/dL and/or a serum triglyceride concentration ≥250 mg/dL Previously identified HA1C ≥5.7 percent, impaired glucose tolerance or impaired fasting glucose.
Polycystic ovary syndrome.
History of vascular disease.